The ketogenic diet (or keto diet) has gained significant attention in recent years as a powerful approach to weight loss, metabolic health, and even neurological benefits. But what exactly is the ketogenic diet, and how does it work? In this article, we will explore the principles of ketosis, the biological impacts of a ketogenic lifestyle, common myths, meal planning tips, and the latest scientific findings supporting its effectiveness.

What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate dietary regimen designed to shift the body’s metabolism from glucose dependence to fat utilization. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake (typically to around 5-10% of total daily calories), the body enters a metabolic state known as ketosis, where it begins to break down fats into ketone bodies to use as energy instead of glucose.
This shift in metabolism has been shown to have a range of effects on the body, from promoting fat loss to enhancing cognitive function (NCBI Bookshelf, 2023).
How Does Ketosis Work?
Under normal dietary conditions, the body primarily relies on carbohydrates for energy. However, when carbohydrate intake is drastically reduced, insulin levels drop, and the liver begins converting stored fat into ketone bodies:
- Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB)
- Acetoacetate (AcAc)
- Acetone
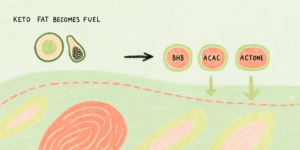
These ketone bodies become the body’s main energy source, fueling the brain, muscles, and other tissues in the absence of glucose. This metabolic adaptation can be beneficial for both weight loss and brain function (MDPI, 2023).
Key Health Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet

1. Weight Loss and Fat Burning
Studies have consistently shown that ketogenic diets are effective for weight loss, often outperforming low-fat diets in clinical trials. This is due to several factors:
- Increased Fat Burning: With insulin levels lowered, fat stores are more readily accessed for energy.
- Reduced Appetite: Ketosis has been shown to regulate hunger hormones like ghrelin, leading to reduced cravings and caloric intake.
- Improved Metabolic Flexibility: The body becomes more efficient at switching between fuel sources (Nature, 2022).
2. Cognitive and Neurological Benefits
The ketogenic diet has been extensively studied for its effects on brain health. Research suggests that ketone bodies provide a more stable and efficient fuel source for the brain, potentially improving memory and focus.
Additionally, ketogenic diets have been used as a therapeutic intervention for neurological conditions like epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease (PubMed, 2023).
3. Improved Blood Sugar and Insulin Sensitivity
One of the most well-documented benefits of the ketogenic diet is its ability to stabilize blood sugar levels and enhance insulin sensitivity. This makes it an attractive option for individuals with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome (NCBI Bookshelf, 2023).
4. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Research indicates that ketones, particularly beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), have potent anti-inflammatory properties. This may contribute to the diet’s beneficial effects on chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis and cardiovascular disease (American Journal of Physiology, 2023).
Common Myths About the Ketogenic Diet

1. Keto is Just About Eating Bacon and Butter
Many people believe the ketogenic diet is only about consuming large amounts of fatty foods like bacon and butter. In reality, a well-balanced ketogenic diet includes healthy fats from sources like avocado, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish, along with moderate protein intake and low-carb vegetables.
2. You Can’t Eat Any Carbs on Keto
While the ketogenic diet does emphasize low-carb intake, not all carbohydrates are forbidden. Many people successfully incorporate fiber-rich, non-starchy vegetables like spinach, kale, and broccoli into their diet.
3. Ketosis and Ketoacidosis Are the Same
Ketosis is a normal, controlled metabolic state, while ketoacidosis is a dangerous condition typically occurring in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Nutritional ketosis does not lead to ketoacidosis in healthy individuals.
Practical Tips for Getting Started with Keto
- Plan Your Meals – Focus on whole, unprocessed foods rich in healthy fats, moderate protein, and low carbohydrates.
- Stay Hydrated – Ketosis can lead to increased water loss, so drinking plenty of fluids is essential.
- Replenish Electrolytes – Sodium, potassium, and magnesium are crucial to prevent keto flu symptoms.
- Track Macros – Keeping track of fat, protein, and carbohydrate intake ensures you stay in ketosis.
- Experiment with Recipes – Enjoy keto-friendly meals like avocado egg salads, cauliflower rice bowls, and almond flour pancakes.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While the ketogenic diet offers numerous health benefits, it is not without its potential drawbacks:
- Keto Flu: Temporary symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, and irritability may occur as the body adapts to using ketones for fuel.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Since many carbohydrate-rich foods are also high in essential vitamins and minerals, careful meal planning is needed.
- Lipid Profile Changes: Some individuals may experience increases in LDL cholesterol, though this varies among individuals (South African Journal of Anaesthesia and Analgesia, 2023).
Conclusion
The ketogenic diet is a well-researched, scientifically supported approach to improving metabolic health, enhancing brain function, and supporting weight loss. By transitioning the body from glucose to fat as its primary energy source, ketosis offers numerous health benefits beyond simple weight management.
Whether you are looking to optimize cognitive performance, manage a medical condition, or simply improve overall health, the ketogenic diet provides a powerful nutritional strategy grounded in science. As always, consulting with a healthcare professional before making major dietary changes is recommended.
 Animal-Based Foods
Animal-Based Foods 


 Fruits & Vegetables
Fruits & Vegetables 

 Nuts, Seeds & Grains
Nuts, Seeds & Grains 


 Beverages
Beverages 

 Oils, Sauces & Condiments
Oils, Sauces & Condiments 


 Packaged & Processed Foods
Packaged & Processed Foods 




